유한회사 in South KoreaYuHanHoeSa
Business Type Information
Basic details about the type of business.
- Country
South Korea (KR , KOR)
- Subregion
- Eastern Asia
- Region
- Asia
- Language
- Korean
- Language Code
- KR
- Abbreviations
- (유)
- Abbreviations transliterated
- (Yu)
- Created date
- Jun 10, 2020
- Last modified date
- Mar 19, 2024
- Tags
Legal Entity Management Made Simple
Start using
Lextree today.
Control even complex legal entities.
Learn more about entity management software
There are five important principles for managing a YuHanHoeSa in South Korea. Those principles are: ownership or business structure, compliance, governance and management, documentation, and notifications.
South Korea (Yu) Ownership and Business Structure
Businesses are structured differently around the world based on the legal and economic system in the jurisdiction. Each type of legal entity is owned, controlled, or formed by people. A YuHanHoeSa is no exception.
As a legal fiction, it is important to know who owns or controls the business. Ownership tracking means identify the people (or other companies) which have a legal or economic interest in the business. Legal and economic rights include the right to vote ("Voting Rights") on important business matters and the right to a share of profits and losses ("Economic Rights"). Not all business types have profits to distribute.
Ownership tracking is important for many reasons. It is important for tax purposes, for compliance with laws and regulations, and for the protection of the business and its owners.
One of the best reasons to track ownership is to create organization charts automatically.
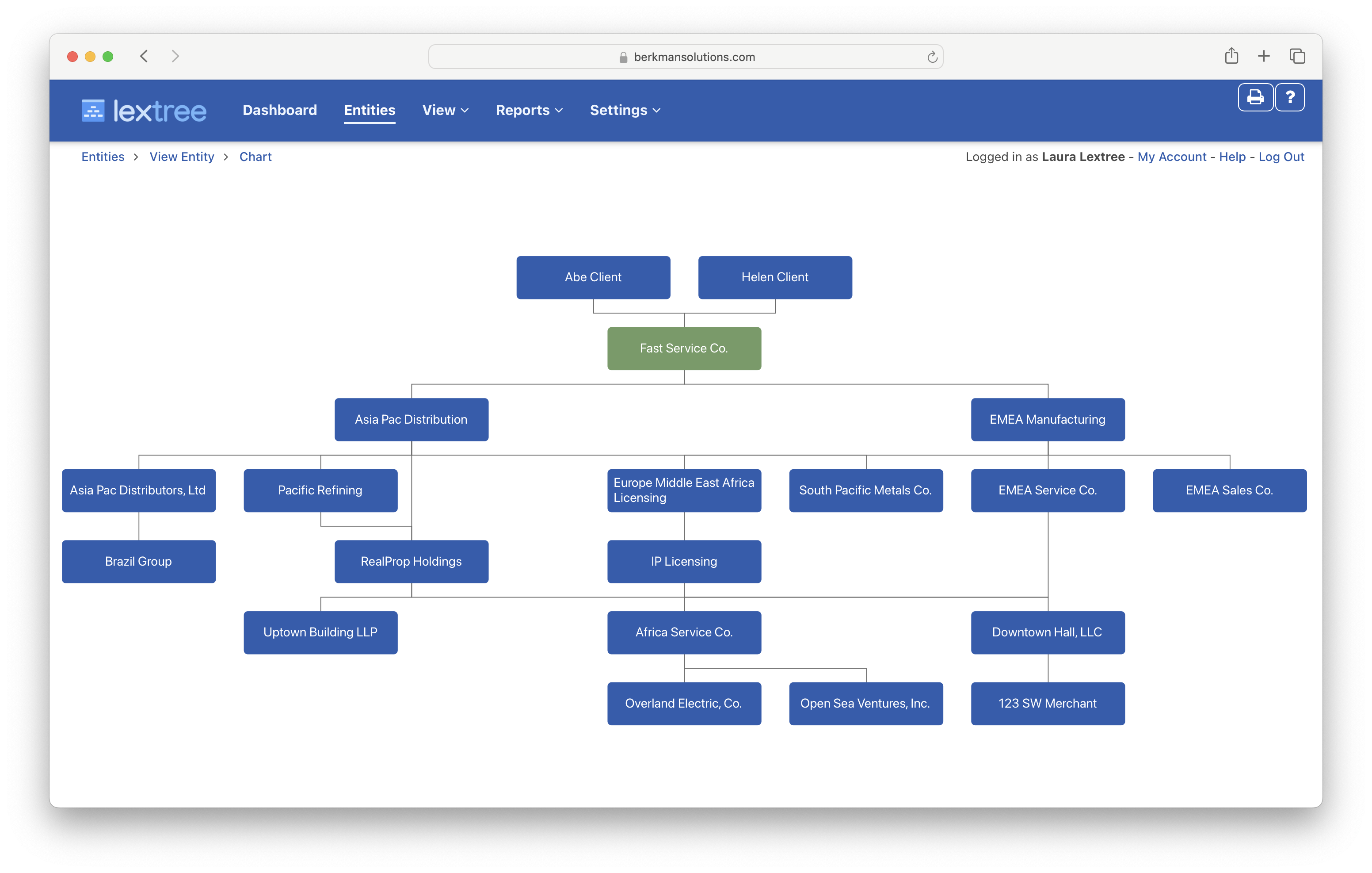
South Korea (Yu) Compliance and Requirements
As a legal entity, a business must comply with national, state or provincial, and local laws. Compliance often means business filing requirements.
Compliance also means following the rules and regulations of the industry in which the business operates. For example, a YuHanHoeSa in South Korea must comply with the laws and regulations of South Korea government. It must also comply with the laws and regulations of the industry in which it operates.
Compliance is important to reduce the risk of fines and penalties.
Compliance tracking for businesses is an ongoing process for the life of the company. Whether it is tracking the annual report or business licenses, entity management software to track compliance is vital.
South Korea (Yu) Governance and Management
Every business has a governance structure. Governance is the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. Governance is important for the success of the business. It is also important for the protection of the business and its owners.
Governance systems, laws, and practices vary across jurisdictions. Think about governance on two levels: the group (for example, a Board of Directors) which sets broad strategy and overseas the management; and the senior managers who direct daily operations of the business.
Governance tracking means knowing who has what title and role in the company. It is also useful, and sometimes required, to track the person's term of service (appointment date and termination date).
South Korea (Yu) Documents and Records
Every business has documents and records that need tracking. Sometimes it is a simple matter of using a document management system. Businesses have special reporting and tracking needs related to documents.
For example, a YuHanHoeSa in South Korea may need to track annual reports, minutes of meetings, and organizational documents.
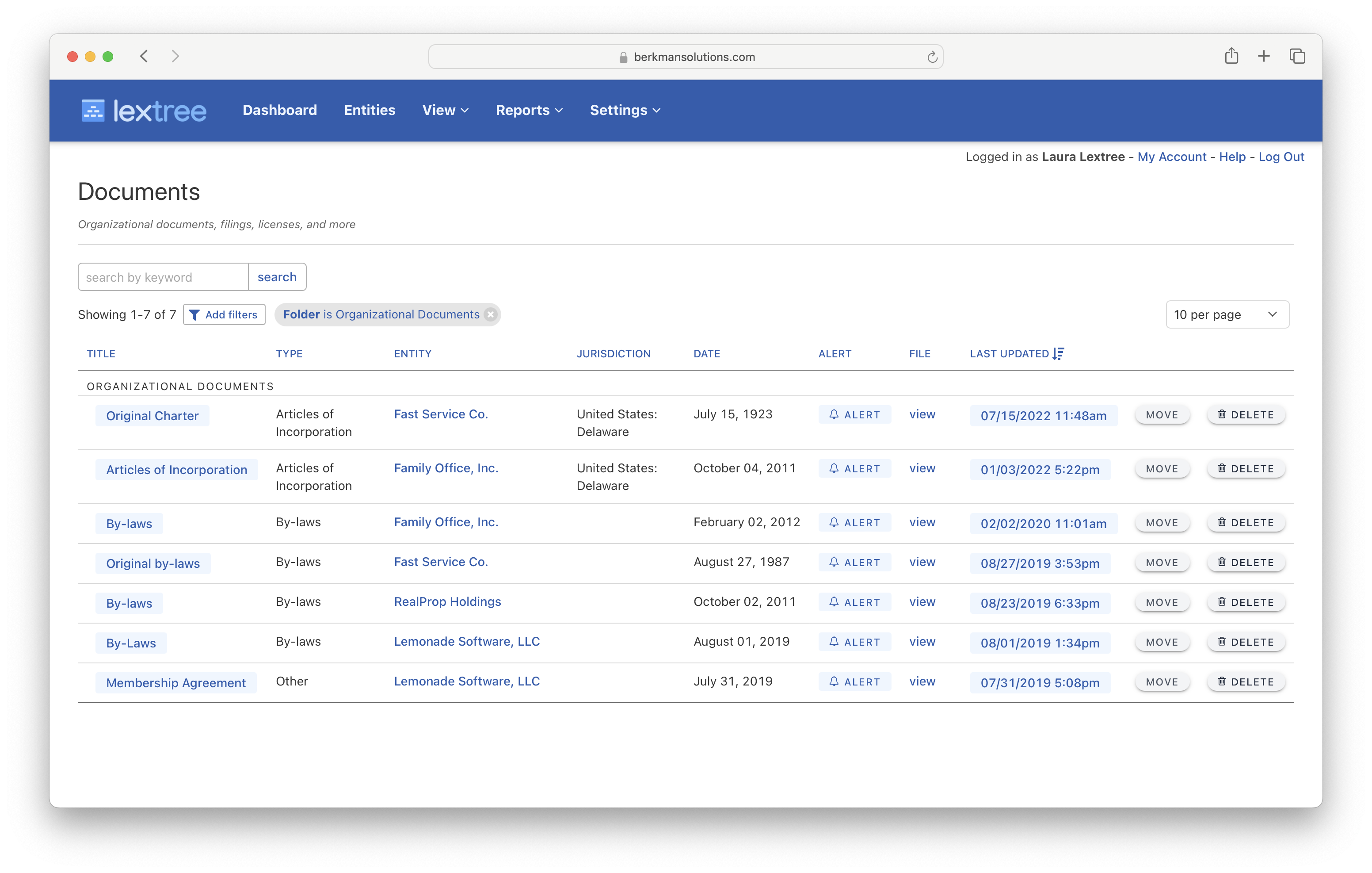
Alerts and Notifications
All of that tracking for ownership, governance, compliance, and documents helps create legal entity reports. More important, however, is that entity management software can send automatic alerts and notifications about critical deadlines.
Conclusion
Managing a YuHanHoeSa in South Korea is a complex task. It requires tracking ownership, compliance, governance, documents, and notifications. Entity management software can help.
References